Have you ever stopped to think about why you feel a certain way in different situations? It’s natural to recognize simple emotions like happiness, sadness, or anger, but as humans, our emotional landscape is far more complex.
Knowing these feelings well is vital for personal growth and fostering relationships. To cope with these, psychologist Robert Plutchik developed the Wheel of Emotions used in mapping out how emotions are related and vary in intensity.
It is through getting to know the wheel that we gain a more profound understanding of our emotional space, we improve our emotional quotient and we have a better life balance. Next, let us discuss how Plutchik’s Wheel can help us better understand our emotions and use them practically in everyday living.
Robert Plutchik, Creator of the Emotions Wheel
Robert Plutchik, a known psychologist was born on October 21, 1927. Passed away on April 29, 2006. He held the position of professor emeritus, at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine. Was also an adjunct professor at the University of South Florida.
Plutchik obtained his Ph.D. From Columbia University. Was highly regarded for his academic contributions. Throughout his career he. Coauthored over 260 articles, 45 chapters, and eight books well as edited seven books.
Plutchik delved into research areas including emotions, suicide and violence studies, and psychotherapy processes. His notable work on the Wheel of Emotions framework continues to have an impact, on psychology.
What is the Plutchik’s Wheel of Emotions?
Robert Plutchik proposed a psychoevolutionary classification of general emotional responses highlighting their essential role in human behavior. He identified eight primary emotions—anger, fear, sadness, disgust, surprise, anticipation, trust, and joy—emphasizing their significant survival value. For instance, fear triggers the fight-or-flight response, crucial for survival.
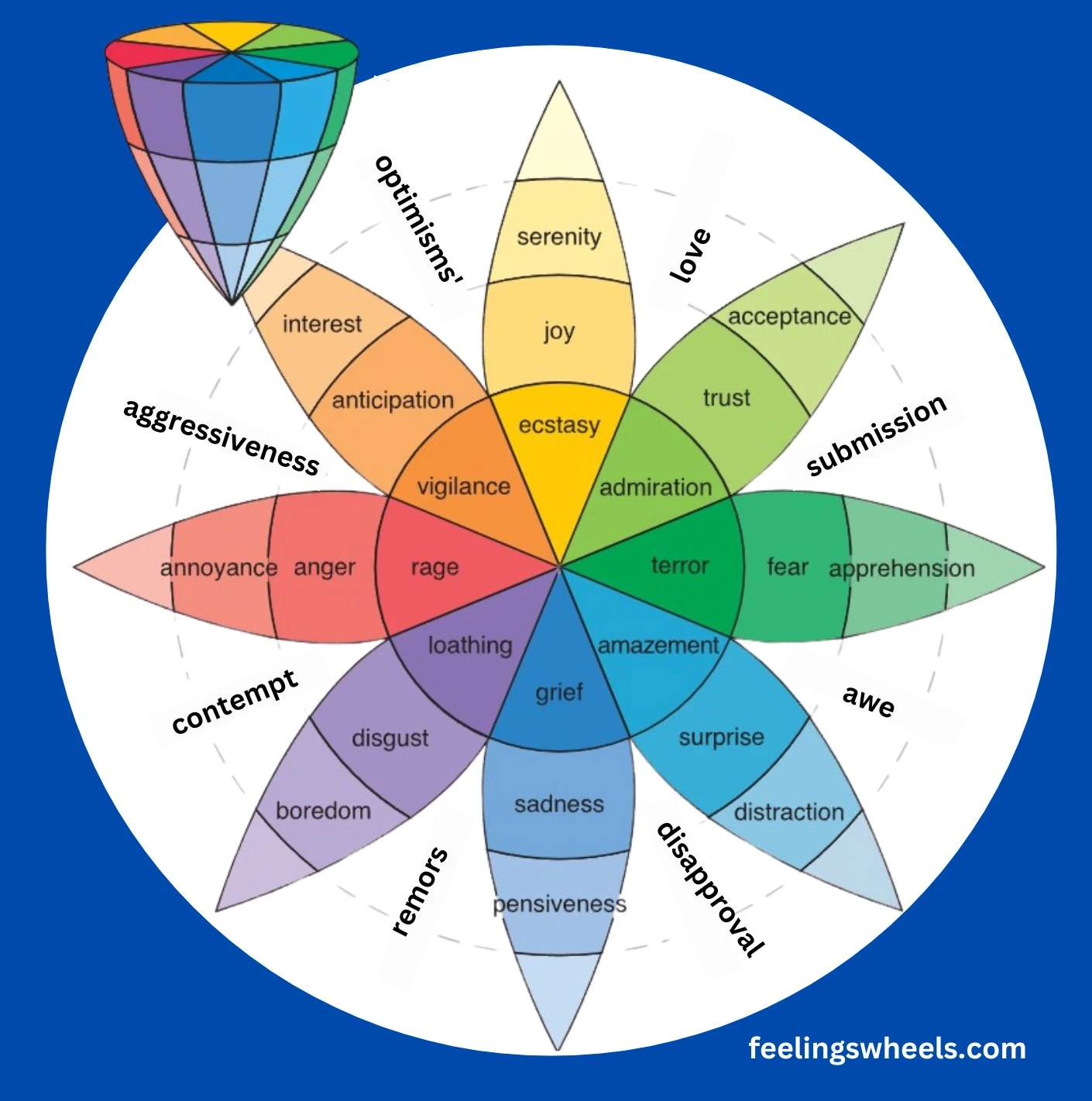
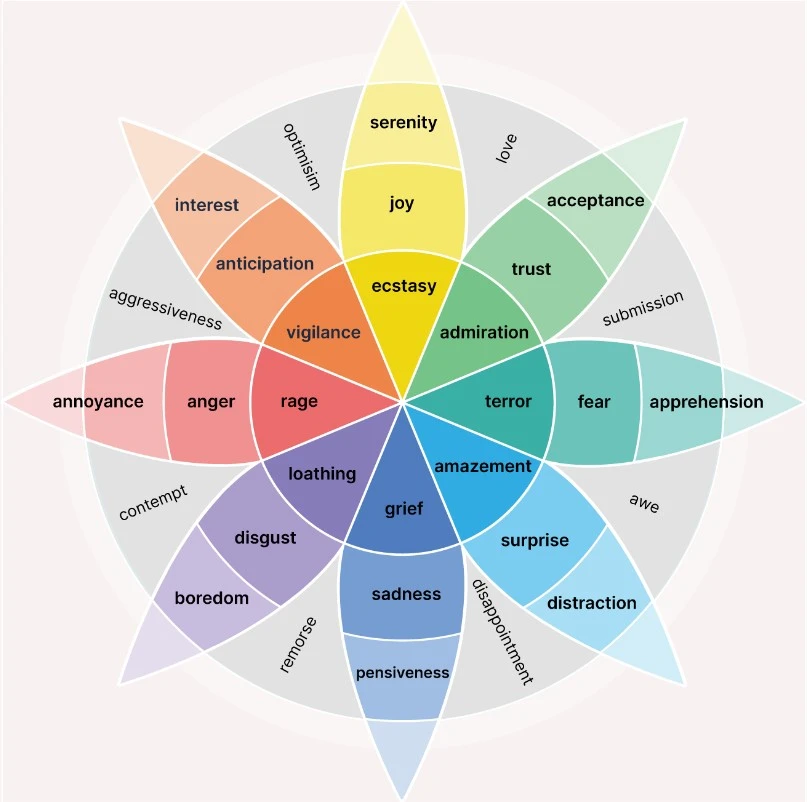
His model, often illustrated as the Wheel of Emotions, organizes these primary emotions based on their physiological purposes. This structured framework akin to an unfolding “ice cream cone,” provides insights into how emotions interact and influence human experiences.
Plutchik’s psychoevolutionary theory of basic emotions posits ten fundamental principles:
- Emotion applies universally across all evolutionary levels, encompassing both animals and humans.
- Emotions have evolved diverse forms of expression across different species.
- Emotions play an adaptive role in helping organisms navigate survival challenges in their environments.
- Despite variations in expression, there are identifiable prototype patterns common to emotions.
- A small set of basic or primary emotions exists.
- All other emotions are combinations or derivatives of these primary states.
- Primary emotions are theoretical constructs, inferred from various evidence sources.
- Primary emotions can be understood in terms of pairs of polar opposites.
- Emotions vary in their degrees of similarity to one another.
- Each emotion can manifest across a spectrum of intensities or levels of arousal.
Read More: emotion vs. feeling: what is the difference
Understanding Plutchik’s Wheel of Emotions
The wheel of emotions is akin to a vibrant flower, consisting of three key components—primary emotions, opposites, and combinations
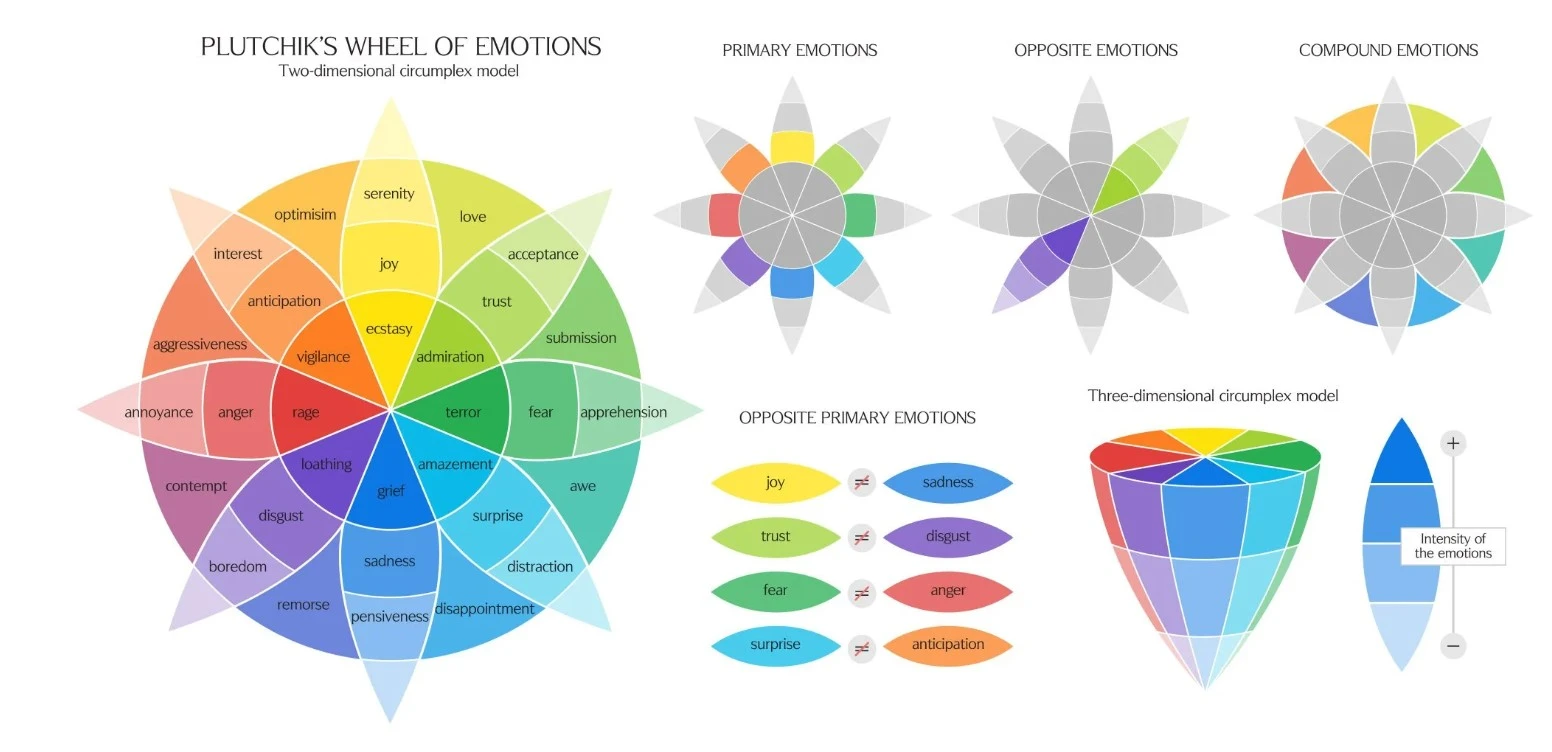
Primary Emotions
At the core, the wheel of emotions consists of eight primary emotions, which are: anger, anticipation, joy, trust, fear, surprise, sadness, and disgust.
opposite emotions: optimism, love, submission, awe, disappointment, remorse, contempt, aggressiveness.
Basic Emotional Pairs on
The basic emotional pairs are as follows:
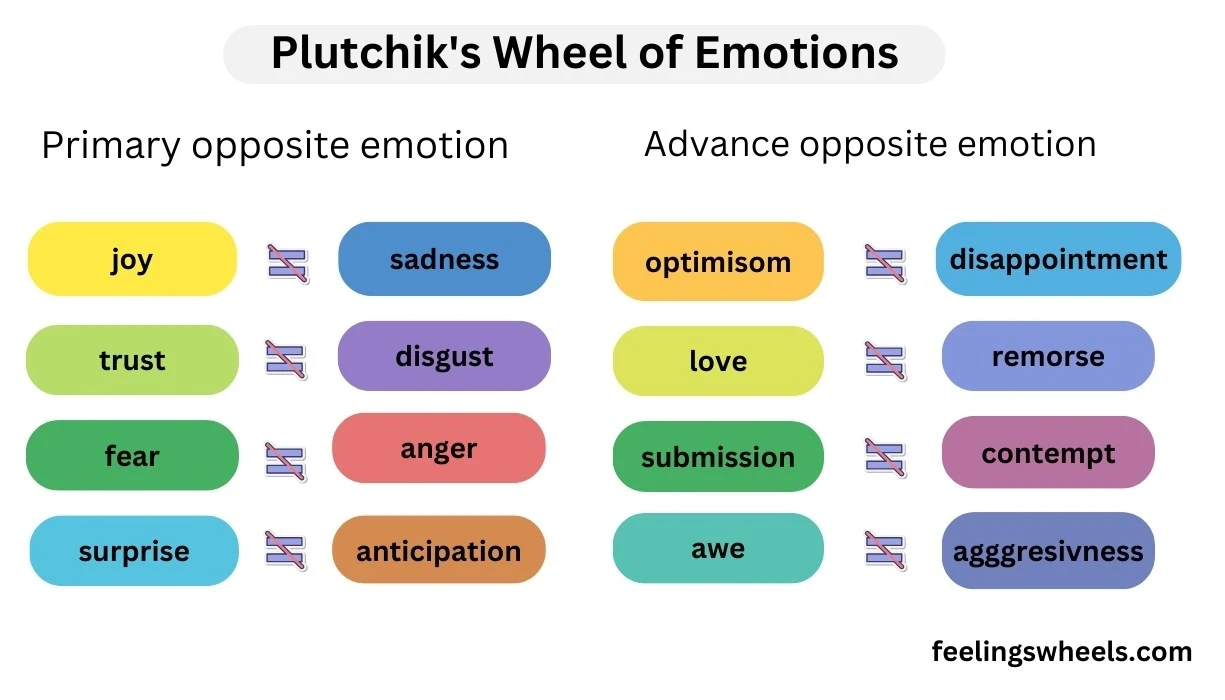
- Joy and Sadness
- Trust and Disgust
- Fear and Anger
- Surprise and Anticipation
Combining Emotions
Combining different core emotions will create new emotions. Some examples include:
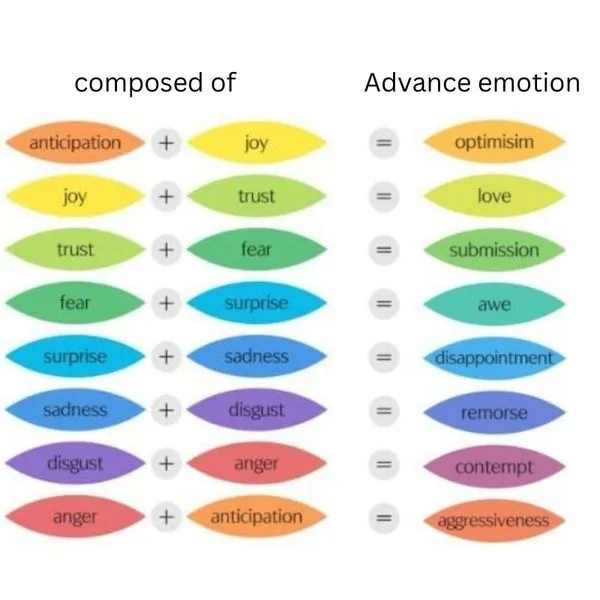
- anticipation + joy = Optimism
- Joy + Trust = Love
- Trust + Fear = Submission
- Fear + Surprise = Awe
- Surprise + Sadness = Disapproval
- Sadness + Disgust = Remorse
- Disgust + Anger = Contempt
- Anticipation + Anger = Aggressiveness
How to use an emotion wheel
An emotion wheel is a tool designed to help individuals identify and understand their emotions. Here’s how to use it effectively:
Step-by-Step Guide:
1. Identify Your Core Feeling:
Start by identifying the broad category of emotion you’re experiencing. These core feelings are usually at the center of the wheel and include basic emotions like joy, sadness, anger, fear, surprise, and disgust.
2. Narrow Down the Emotion:
Once you have a general idea, look outward to the next ring of the wheel to narrow down your emotion. For example, if you identify your core feeling as anger, the next ring might include emotions like frustration, irritation, or hostility.
3. Pinpoint Specific Emotions:
Continue moving outward to the more specific emotions in the outer rings of the wheel. This helps identify the exact emotion you’re feeling. Using the previous example, frustration might narrow down further into feelings like annoyance or aggravation.
4. Reflect on the Identified Emotion:
Take some time to reflect on the identified emotion. Ask yourself questions like, “Why am I feeling this way?” or “What triggered this emotion?” This can help understand the underlying causes and patterns.
5. Express and Process the Emotion:
Use the identified emotion to communicate more effectively with others or to process it internally. For instance, if you realize you are feeling overwhelmed (a combination of fear and stress), you can seek specific support or coping strategies.
Practical Tips:
- Use it Regularly: Make a habit of checking in with the emotion wheel daily or during moments of strong emotions to better understand your feelings.
- Journal Your Findings: Write down your emotions and reflections. This practice can help you track patterns and triggers over time.
- Share with Others: Use the emotion wheel in conversations with friends, family, or therapists to articulate your feelings more clearly.
Applications:
- Personal Growth: Helps in emotional self-awareness and personal development.
- Therapy: This can be a useful tool in therapeutic settings to help clients articulate their feelings.
- Conflict Resolution: Assists in resolving conflicts by promoting better understanding and communication of emotions.
- Education: Teachers and educators can use it to help students learn about emotions and improve emotional literacy.
FAQ’S
which emotion is the opposite of trust on robert plutchik’s wheel of emotions?
On Robert Plutchik’s Wheel of Emotions, the opposite of trust is disgust. The wheel positions trust and disgust as opposing emotions, reflecting the way positive connection and repulsion contrast each other in human emotional responses. This opposition helps illustrate the complex dynamics of human feelings.
match the feelings to its correspondent combination. optimism awe contempt fear + surprise arrowright anticipation + joy arrowright disgust + anger arrowright
To match feelings with their combinations: Optimism pairs with anticipation + joy, awe with fear + surprise, and contempt with disgust + anger. These combinations reflect the nuanced ways emotions interact, helping to identify complex feelings by connecting them to their corresponding emotional blends.
conclusion
In conclusion, Plutchik’s Wheel of Emotions serves as a powerful tool for enhancing emotional intelligence. By helping individuals identify understand, and articulate their feelings it fosters better self-awareness and communication.
Integrating this tool into daily life can lead to improved mental well-being and more meaningful interpersonal connections.
reference: Wikipedia