Let’s dive into the fascinating world of emotions. Imagine a colorful carousel spinning in your mind, each emotion a distinct horse. Feelings, like quick rides, come and go—joy when you win a game, sadness when you miss someone.
Moods, on the other hand, linger like background music, shaping your day—think of them as the weather of your emotional landscape. And then there are emotions, the grand symphony—the intense chords of love, anger, or fear that resonate deep within you. Buckle up as we explore the dimensions of emotions and feelings!
In a nutshell, emotions can transform into moods, moods can influence emotions, and feelings serve as our interpretation of those emotions
1. Understanding Emotions

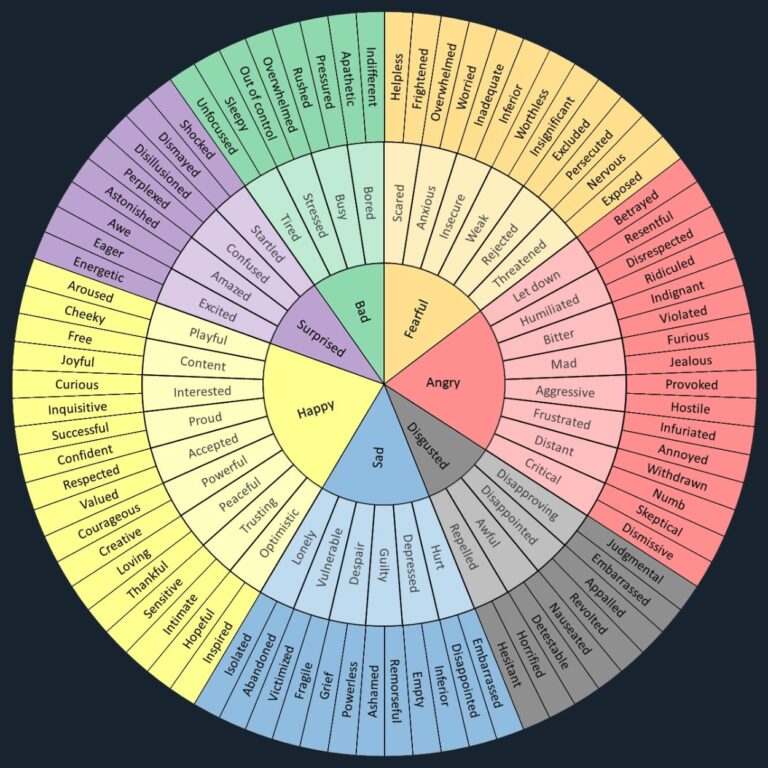
Emotions are complex psychological and physiological responses to stimuli or situations. They are typically intense and short-lived, prompting specific reactions. Emotions are universal and are often categorized into basic types such as happiness, sadness, fear, anger, surprise, and disgust. They can trigger physical reactions, like a racing heart or sweating, and drive behaviors, such as fleeing from danger or smiling at a joke.
Example: Seeing a snake might instantly trigger the emotion of fear, causing your heart to race and your body to prepare to run away. This immediate and intense reaction is characteristic of an emotion.
2. Understanding Feelings

Feelings are subjective experiences that arise in response to emotions. They are the personal interpretation and internalization of emotions. For example, you might feel happy, sad, anxious, or excited. Feelings are often influenced by individual perceptions, experiences, and thoughts. They can be fleeting or last longer, depending on the intensity of the underlying emotion and the individual’s mental state.
Example: If you receive a compliment from a friend, you might feel appreciated or pleased. This feeling is your personal response to the emotion of happiness triggered by the compliment.
3. Understanding Moods

Moods are more prolonged and less intense than emotions. They are generalized emotional states that are not necessarily tied to a specific trigger. Moods can last for hours, days, or even longer and can influence a person’s overall outlook and behavior. Unlike emotions, which can change quickly in response to events, moods are more stable and persistent.
Example: If you wake up and feel down for no particular reason, you might describe yourself as being in a bad mood. This mood can affect your interactions and activities throughout the day, even if no specific event caused it.
Key Differences Between feeling vs emotion
| Aspect | Feelings | Emotions |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Fleeting can change quickly. | Complex and deeper psychological responses. |
| Duration | It can be more general and pervasive. | More enduring and can persist over time. |
| Trigger | Fleeting can change quickly. | You are experiencing long-term self-confidence from consistent achievements. |
| Example | Feeling proud after a personal achievement. | I am experiencing ongoing stress due to chronic work pressure. |
| Example | Feeling irritated after a minor inconvenience. | Experiencing ongoing stress due to chronic work pressure. |
| Example | Feeling excited about an upcoming event. | Experiencing underlying anxiety that affects various aspects of life. |
Flow Chart: emotion vs feeling vs mood
emotion vs feeling vs mood
Let’s explore how feelings, emotions, and moods interact within our inner world. Imagine them as a trio:
Emotions: These are the intense soloists—the sudden joy, fear, or anger that steal the spotlight. They’re like lightning bolts, brief but powerful.
- Duration: Emotions are brief and typically last for a short period, like a few seconds or minutes.
- Intensity: Emotions are generally more intense and pronounced. For example, fear when startled by a loud noise.
- Example: Feeling happy after receiving a compliment, which fades quickly as you move on
Feelings: Think of feelings as the harmonies—the subtle notes that linger. They emerge from emotions, shaped by our thoughts. Whether it’s happiness after a compliment or sadness after a goodbye, feelings color our days.
- Duration: Feelings can persist for hours, days, or even longer.
- Intensity: Feelings are subjective experiences shaped by our interpretations.
- Example: Feeling loved or appreciated by someone, which may last beyond the initial emotion
Moods: Moods set the stage—the emotional climate. Whether it’s a sunny optimism or a stormy melancholy, moods influence our overall experience.
- Duration: Moods can last for hours, days, or even longer.
- Intensity: Moods are typically less intense but can have longer-lasting effects.
- Example: Waking up feeling cheerful, which influences your entire day and interactions with others.
Feelings vs. Emotions: Understanding the Subtle Differences
At first glance, feelings and emotions might seem like interchangeable terms. However, these two aspects of our inner experiences have subtle yet significant differences. Understanding these differences can help us navigate our emotional landscape with greater clarity and precision.
Feelings: Fleeting and Situational
Feelings are the immediate and subjective interpretations of emotions. They arise from our thoughts about the emotional experiences we encounter. Feelings are often fleeting and can change rapidly depending on the situation.
For instance, if someone compliments your outfit, you might feel a brief moment of happiness or satisfaction. This feeling is your personal response to the emotion of happiness triggered by the compliment. Feelings are influenced by our perceptions and past experiences, making them unique to each individual.
Feelings are also situational. They can shift quickly based on new information or changes in our environment. If that same person who complimented your outfit later criticizes your work, your feeling of happiness might quickly turn to frustration or disappointment.
Emotions: Deeper and Longer-Lasting
Emotions, on the other hand, are more profound and enduring than feelings. They are complex psychological and physiological responses to stimuli or events. Emotions are often intense and can have a lasting impact on our overall well-being.
For example, the emotion of grief after losing a loved one can be overwhelming and persist for a long time. This deep emotional response involves various feelings such as sadness, longing, and even anger. Emotions are rooted in our biology, with specific chemicals and neural pathways in the brain triggering these responses.
Emotions tend to be more stable than feelings. While feelings can fluctuate from moment to moment, emotions provide a more consistent backdrop to our experiences. The emotion of love, for instance, might remain constant over time, even as the specific feelings associated with it (joy, contentment, frustration) change.
conclusion
Knowing the differences between emotions, feelings, and moods enhances our personal experiences and knowledge about ourselves in terms of our emotions. Emotions refer to our immediate, intense responses to stimuli, accompanied by physiological and cognitive alterations.
Feelings are our personal interpretations of what these emotions mean, taking into consideration our thoughts and past experiences, and are usually short-lived.
Conversely, what we call moods are long-term emotional flavors that have an influence on general mentality as well as actions people take. Knowing them enables us to handle our inner world therefore we begin to live a meaningful life with good mental health.
Hence we can respond with valiance and understanding to any emotional experience after noticing these fine details.